* Please refer to the English Version as our Official Version.
* Please refer to the English Version as our Official Version.
On March 24th this year, 94 year old Gordon Moore passed away at his home in Hawaii - a metaphor of an era: is Moore's Law also leaving us with Mr. Moore?
Undoubtedly, the evolution of the number of single chip transistors and process geometry closely related to Moore's Law is entering a "singularity moment". At the same time, the demand for high computing power in terminal applications is still continuously pushing up the size of single chip Dies. Under the physical constraints of the mask wall, many chip design manufacturers are facing increasingly severe challenges in balancing chip process and yield flow costs, as well as strict market time.
For decades, the development history of the semiconductor industry has always followed the philosophy of "Occam's Razor", and the entire process from design to manufacturing needs to avoid the futility of "making wheels repeatedly". The industry calls for repeated design and reuse to improve chip development efficiency, eliminate redundant design costs, and give rise to the rise of IP modules. Currently, facing the pressure of Moore's Law approaching its limit, the integration of advanced packaging heterogeneous systems with 3DIC Chiplet has become a focus of discussion in the industry. This innovative system has not only brought many breakthroughs in the design, packaging, manufacturing, and application of Chiplets, but also opened a window for a group of high-speed Chiplet interface IP suppliers. For a time, Chiplet technology was widely regarded as the Aladdin's magic lamp that continued the vitality of Moore's Law. Xin Yaohui Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Xin Yaohui") is one of the "burners" of this "magic lamp", providing strong support for the key role of interface IP.
As one of the few domestic suppliers with complete D2D and C2C IP solutions, after nearly three years of unremitting efforts, we have taken the lead in independently developing multiple industry standard interface IPs in China and have been adopted by top customers.
Those who are skilled in warfare seek the potential, and the potential follows the people. The development path of Xin Yaohui is multi-dimensional and three-dimensional, whether it is in the top-down top-level design, participation in interface standard formulation, or in the bottom-up technology implementation practice and cutting-edge exploration in response to various harsh challenges of interface IP, we always maintain a high degree of professionalism and are wholeheartedly committed to providing customers with the best technical support in terms of product reliability.
First class enterprise setting standards: Xin Yaohui continuously promotes the industrialization of domestic CCITA standards
The principle of chiplet is to divide the chip into different small chips and interconnect them. In an ideal state, the interconnection efficiency between multiple chips needs to be on par with the interconnection efficiency within a single chip. This requires the interconnection system of the internal bus of the chip to be "ported" and copied to the inter chip interconnection. Therefore, the inter chip interface can be said to shoulder the heavy responsibility. The strict standards and huge demand for high-speed interconnection between chips are stimulating the booming development of the interface IP market. According to the latest data presented by Eric Esteve, the author of the annual authoritative "Design IP Report", who was interviewed by Jiwei, the market share of interface IP in many IP categories has increased from 18% to 25% in the past five years. Last year, the market revenue of the top five interface categories such as USB, PCIe, and DDR was $1.44 billion, and it is expected to double in the next five years. Esteve also revealed to Aijiwei, "We have great confidence in the market forecast for future high-speed IP interfaces, and the error rate has never exceeded 5%."
The heroes compete for the deer, and those with high skills will succeed. Although there has been a serious discussion in the industry about the collaborative ecosystem of Chiplet technology in the chip field for over a decade, the history of its commercial implementation is not long. Zeng Keqiang, Chairman of Xin Yaohui, once made a judgment that the overall transformation of the industry chain driven by Chiplet technology needs to go through three stages: early stage, growth stage, and mature stage.
In the early stage, which is the "bulk" stage of chip splitting and corresponding advanced packaging definition protocols, unified standards urgently need to be clarified and determined; The growth stage is the stage where some units of Chiplet chips iterate on the process and find the optimal solution. At this time, the process and interconnection standards are also rapidly and gradually forming and unifying; Zeng Keqiang predicts that the Chiplet ecosystem will only truly enter the "IP hardening era" around 2027, when a group of Fabless companies, active substrate suppliers, and EDA companies that support integrated Chiplets will emerge. The IP ecosystem surrounding the Chiplet industry will be more three-dimensional and full, and the collaboration between relevant upstream and downstream suppliers will also be more systematic.
Image001.png
In recent years, the mainstream international Chiplet D2D protocol standards have gradually converged and concentrated into four types: XSR, BOW, OpenHBI, UCIE, etc. If we comprehensively evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of these standards in five dimensions: bandwidth density, energy efficiency ratio, line spacing, delay, and bit error rate, we will find that UCIE gradually wins in terms of industry acceptance with better combinations of bandwidth, energy efficiency, and delay. It can define logical PHY, training mechanism, initialization sequence, sideband, and link control, and can reuse and inherit mature UCIE and CXL ecosystems, Received praise and support from numerous design companies, wafer fabs, and packaging factories.
However, UCIE has higher requirements for IP implementation and packaging processes, and due to some objective reasons such as differences in Chinese and foreign processes and fragmentation of international standards, there is an urgent need for the localization of standards. Therefore, the CCITA standard, which is suitable for the domestic industrial chain and needs, has emerged at the right time. In October 2022, Xin Yaohui undertook the key research and development project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and as a member of the national team, focused on promoting the industrialization of the Chiplet standard CCITA in China. This standard defines parallel and serial ports, which are compatible with UCIE. At the same time, in the packaging process, CCITA's Chiplet standard mainly adopts technologies that can be implemented domestically, fully considering domestic practical applications and actual packaging production capacity.
The international mainstream and localization of UCIE's CCITA standards are in line with the trend, which has made domestic leading interface IP manufacturers aware of the importance of developing their own standards for the domestic environment and ecology. Pure technical standards are just floating towers, and a close combination of technology and business models is needed to explore a feasible path for commercial implementation. With deep accumulation in interface IP related technology, Xin Yaohui is actively involved in the formulation of CCITA protocols while also synchronously developing related products.
Xin Yaohui's arsenal: calmly facing many challenges of high-speed Chiplet interface IP
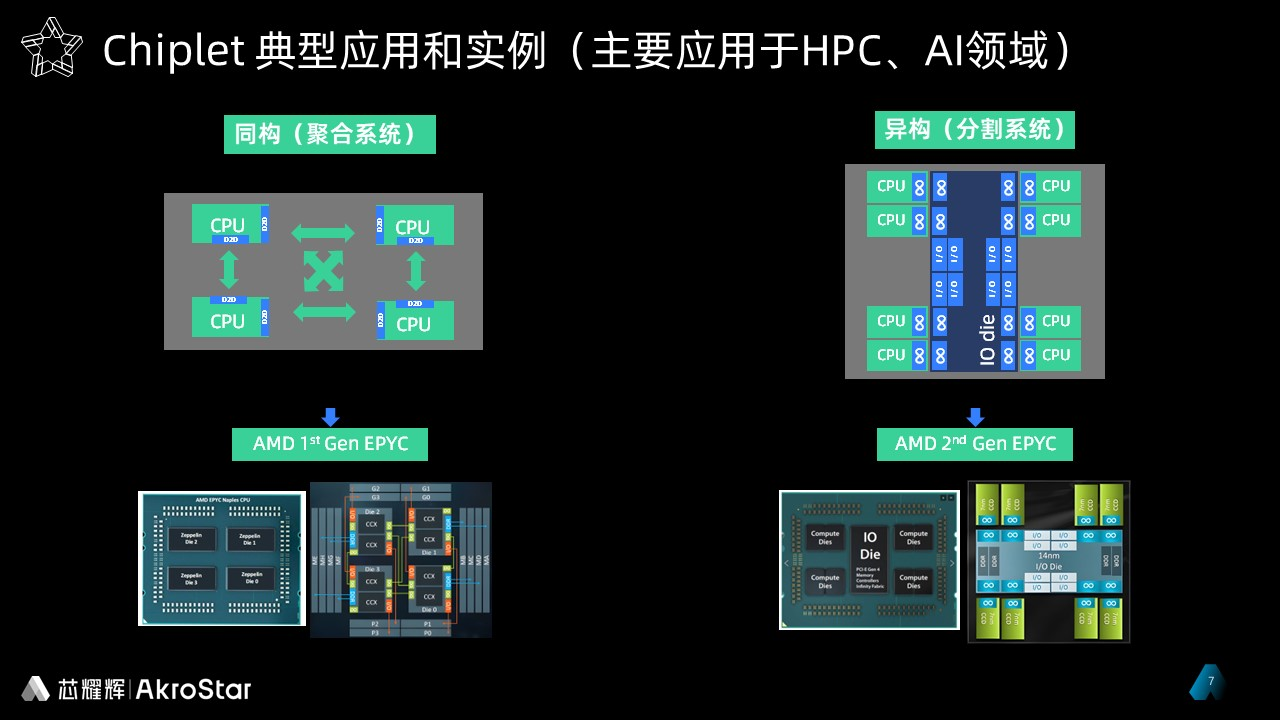
As mentioned earlier, traditional single-chip integrated SoC requires synchronous iteration of different functional modules on the chip due to its unified process, resulting in long chip development time and a large number of defects. Chiplet technology can achieve functional segmentation, process differentiation, and selective iteration of some unit processes, which can accelerate the product launch cycle, reduce the number of re flow and packaging, and thereby reduce the investment cost and development risk of chip companies. In other words, Chiplet can optimize the process of some units on the chip, select the most suitable process for different functions, and under the guidance of this exemplary technical route, extend two commercial field use cases: homogeneous (aggregation system) and heterogeneous (segmentation system).
Isomorphism extends computing power through the implementation of high-speed interface IP and advanced packaging, using the same Die design, suitable for low latency and low error rate application scenarios such as CPU, TPU, AI SoC, etc; "Heterogeneity" refers to the differentiation of chip functions, achieving an organic combination of "heterogeneity" and "structure" - Dies responsible for advanced processes with high computing power and performance and Dies responsible for mature processes with distinctive functions are packaged together. These two most typical practical cases can be demonstrated in detail through the AMD server CPU Epyc series.
The first generation AMD EYPC used isomorphic methods to aggregate four Dies with the same design principle, all of which used the 7nm process. Through the interconnection of multiple Dies, a scalable system was constructed, which reduced the complexity of a single chip while improving computing power and manufacturing success rate; In the second generation of EYPC, the chip functions were divided into CCD Compute Core Die and IO Die, with the former responsible for high-performance computing and the latter for specific functions, achieving a clever integration of different advanced and mature process chips.
High speed interface and advanced packaging dual track drive, a large chip integrates multiple Dies through isomorphic or heterogeneous methods, achieving power expansion. It also puts higher requirements on the portability, standardization, compatibility, low latency, and low bit error rate of the interface. The Chiplet technology pioneers represented by AMD and MediaTek are bound to drive further collaborative development between high-speed interface IP suppliers and packaging and testing factories.
Although Chiplet technology has become a consensus choice for the semiconductor industry under the gradual slowdown of Moore's Law, it still faces many challenges to this day. High speed IP interface suppliers represented by Xin Yaohui recognize that Chiplet is not an independent technology point, but a complex comprehensive technology system that requires joint efforts from all aspects of the entire industry chain. The continuous promotion of this technology depends on the coordinated development of the entire industry chain.
During an interview, Zeng Keqiang, Chairman of Xin Yaohui, stated that the challenges of Chiplet development can be summarized into two dimensions: pure technological challenges at the microelectronics level and challenges in the ecosystem. Firstly, Chiplets themselves integrate advanced packaging technologies that require high-density and high bandwidth wiring, which involves upgrading the number of wiring and packaging materials between multiple Chiplets, resulting in material mismatch problems caused by an increase in material quantity and variety. Pure technical challenges also include D2D transmission between chips, requiring small area, low power consumption, and high bandwidth high-speed interface design, At the same time, the industry also needs to establish a standardized specification to solve communication difficulties between different chips, and so on.
The second major challenge is related to design methods and system architecture. The system segmentation design brought by Chiplet corresponds to the design verification process and methods of dividing a complete large system into multiple Chiplets. This requires collaborative work with EDA tools, as well as a complete design methodology to ensure the effectiveness of the splitting.
The philosopher has a saying: The owl of Minerva only takes off after dusk. Industrial competition is not always a process that unfolds from basic research to industrialization. Strong downstream industrialization capabilities often have a reverse impact on the direction of basic technological routes. Multiple technological factors provide customers with a concrete reference frame when weighing D2D and C2C technology routes, such as chip system performance requirements (such as latency, energy consumption, total bandwidth, etc.), chip physical implementation limitations (such as chip face width, bump pitch), and packaging selection and design limitations (such as packaging layers, packaging thickness, line width and line spacing, etc.).
As a leading domestic advanced interface IP supplier, Xin Yaohui has complete D2D (Die to Die) and C2C (Chip to Chip) solutions. Under the Chiplet technology framework, Xin Yaohui provides multi-dimensional and comprehensive solutions that can meet different packaging, interconnection, and application needs, continuously meeting customers' needs for optimal performance and flexibility. Specifically, with the Chiplet D2D solution, whether it is long-distance interconnection, ultra short distance high-speed communication, or different packaging levels of requirements, Xin Yaohui can accurately match user application scenarios.
In terms of medium to long distance interconnection, Xin Yaohui can provide a "long range" solution designed for long-distance interconnection between PCBs and chips, as well as between chips. In terms of ultra short distance high-speed interconnection, Xin Yaohui's 112G XSR (Chiplet to Chiplet Ultra Short Distance Interconnection) solution can stand out, and it has excellent performance in tight interconnection between chips. Of particular note, Xin Yaohui's D2D UCie product has been iterated, evolving from UCie 8G to UCie 16G, and can demonstrate excellent performance in various advanced packaging. It supports the RISC-V MCU Based Firmware training architecture, which can independently complete PHY initialization, parameter negotiation, training, and ATE testing. It also supports periodic PVT compensation and calibration mechanisms, and has an optimized channel width architecture, It can adapt to various packaging forms and high-density die routing.
Not a single breakthrough, Xin Yaohui's global perspective in the field of high-speed interface IP
From many complex elements such as technology, market, users, and innovation, we can glimpse Xin Yaohui's holistic approach and multidimensional perspective on the development philosophy of Chiplet interface IP. Specifically, this perspective can be expressed from three dimensions: chip design, system design, and production testing.
To create a series of competitive Chiplet interface IP solutions, Chiplet technology must be understood as a complete system design. In addition to PHY IP, Xin Yaohui's solution also includes PHY, controller, and subsystems that integrate PHY and controller together. At the same time, Xin Yaohui also provides technical support such as interposer design, packaging design, PCB design, and 3D packaging simulation, as well as a complete testing plan, to support the efficient operation of customer Chiplet products in multiple aspects, achieving high performance, low power consumption, and low latency, helping different customers to obtain the best PPA that suits their needs.
In order to accelerate the time to market of customer chips and the success rate of a single chip, Xin Yaohui did not push the challenge of Chiplet technology towards system design and production testing to adapt to IP, but instead "went against the current" and solved these challenges at the source of IP design. We can understand Xin Yaohui's mastery of IP technology from the perspective of how enterprises can ensure signal integrity and power integrity when dealing with advanced Chiplet D2D packaging, as well as from the KGD testing process.
The D2D packaging requires more urgent signal integrity, and in order to connect various chip units, it is necessary to traverse the deep packaging circuit through numerous Via, which brings serious signal crosstalk problems and may lead to data distortion and errors. Xin Yaohui has established a comprehensive model of transmitter, receiver, and channel to simulate the frequency response of real channels. This helps to better apply frequency response parameters to the Chiplet model, which is expected to bring important value in solving this problem; The integrity of the power supply is closely related to signal integrity. Xin Yaohui takes the on die cap (ODC) component, which plays a crucial role in high-speed interface design, as the entry point. Through clever power link design and optimized application of ODC, it ensures the stable operation of the entire system,